Thyroid disease
Thyroid disease refers to a group of conditions that occur when the thyroid gland does not produce the correct amount of thyroid hormones required for normal body function. The thyroid is a small, butterfly-shaped gland located in the front of the neck, and it plays a crucial role in regulating metabolism, energy levels, body temperature, and overall hormonal balance. When thyroid hormone levels become imbalanced, it can significantly affect many systems in the body.
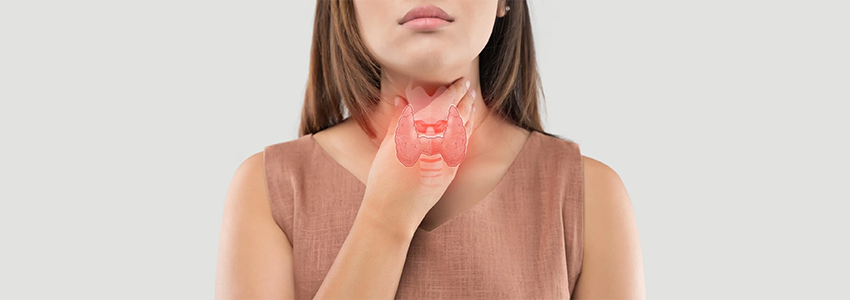
Common symptoms of thyroid disorders include persistent fatigue, unexplained weight gain or weight loss, changes in heart rate, sensitivity to heat or cold, hair thinning, dry skin, mood changes, and difficulty concentrating. These symptoms can vary depending on whether the thyroid is underactive (hypothyroidism) or overactive (hyperthyroidism). Because symptoms often develop gradually, thyroid disease may go undiagnosed without proper medical evaluation and testing.
Diagnosis typically involves blood tests to measure thyroid hormone levels and assess thyroid function. Once diagnosed, treatment is tailored to the specific condition and individual needs. Management options may include hormone replacement therapy, medications to regulate hormone production, lifestyle modifications such as balanced nutrition and stress management, and in some cases, surgical intervention.
With appropriate treatment and regular monitoring, most thyroid conditions can be effectively managed, allowing patients to maintain a healthy and active lifestyle. Early detection, personalized care, and ongoing medical supervision are essential in preventing complications and ensuring long-term well-being.

